publications
2024
-
 Álgebras, grupos e grafosHenrique Assumpção2024
Álgebras, grupos e grafosHenrique Assumpção2024@mastersthesis{assumpcao2024algebras, author = {Assumpção, Henrique}, title = {Álgebras, grupos e grafos}, school = {Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais}, year = {2024}, type = {Undergraduate Thesis}, advisor = {Gabriel de Morais Coutinho}, keywords = {Álgebras semissimples, Teorema de Wedderburn, Otimização semidefinida}, }
2022
-
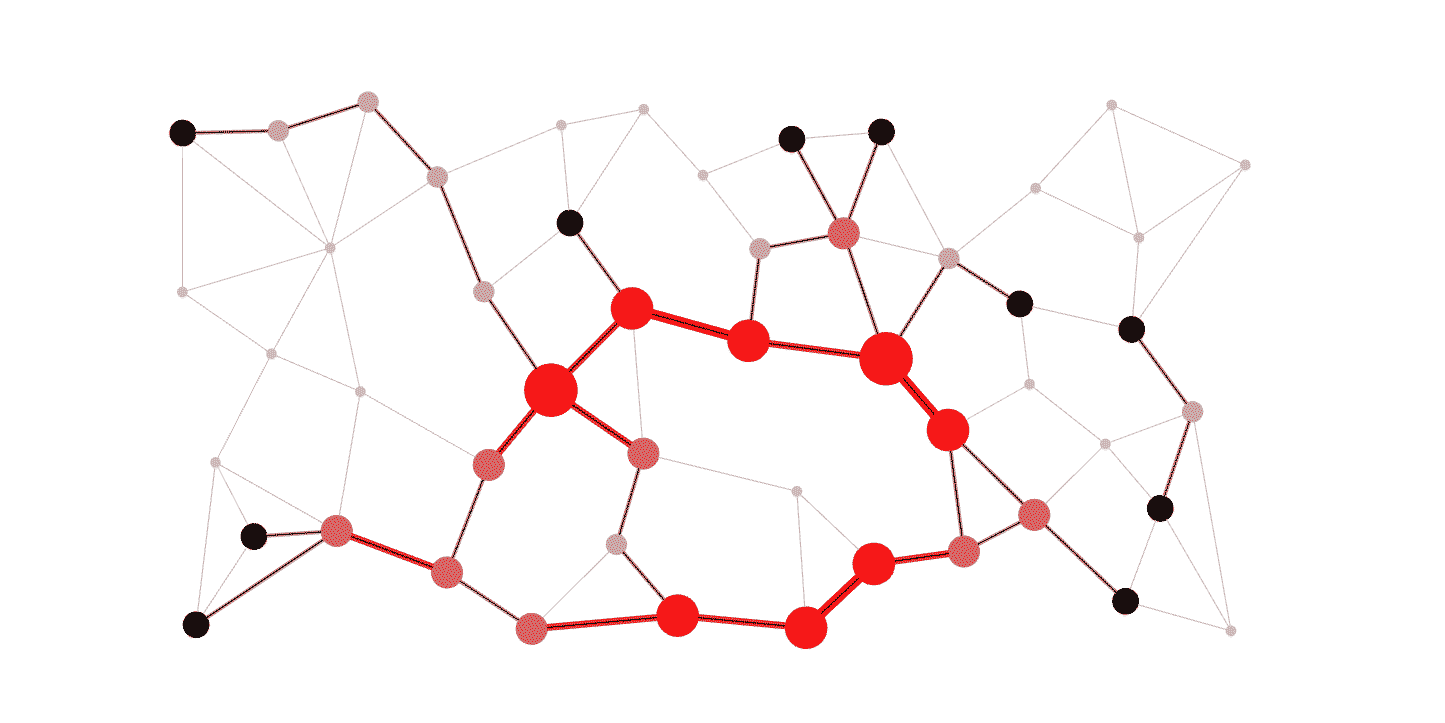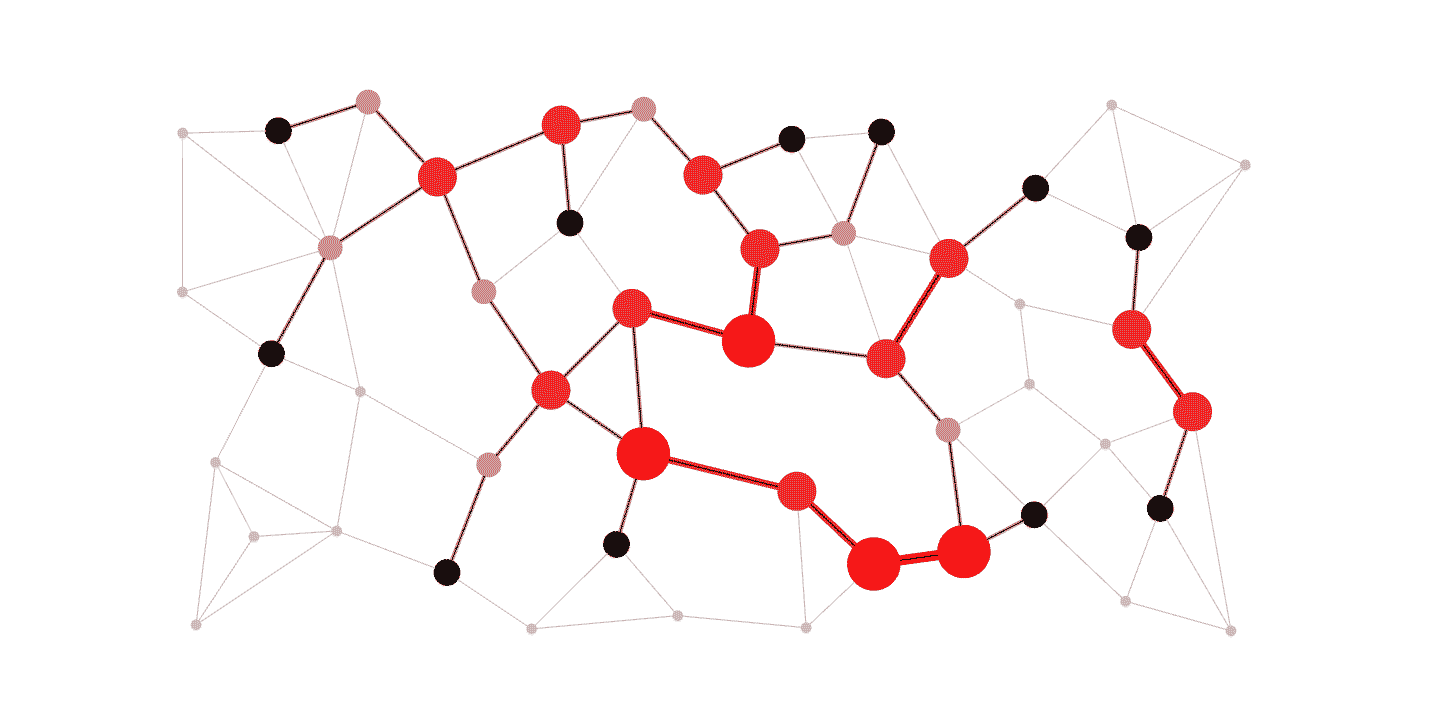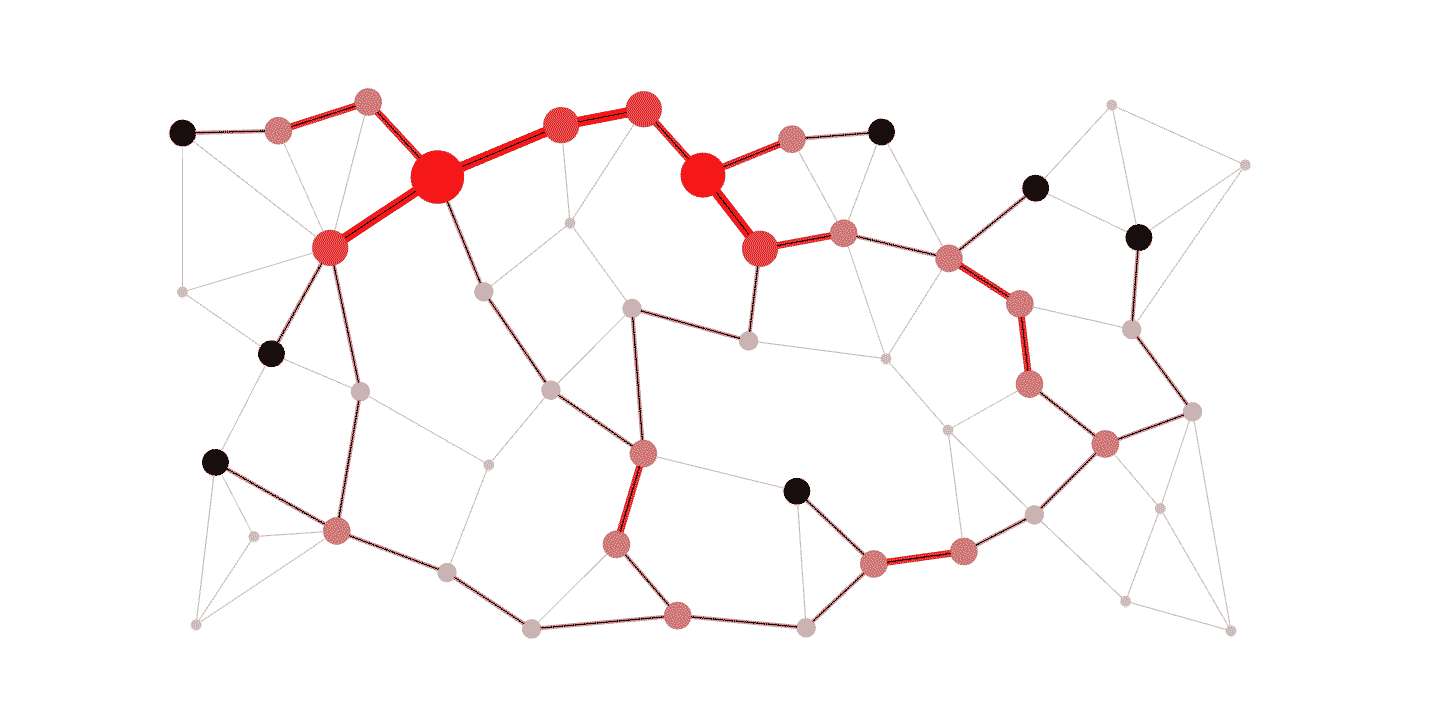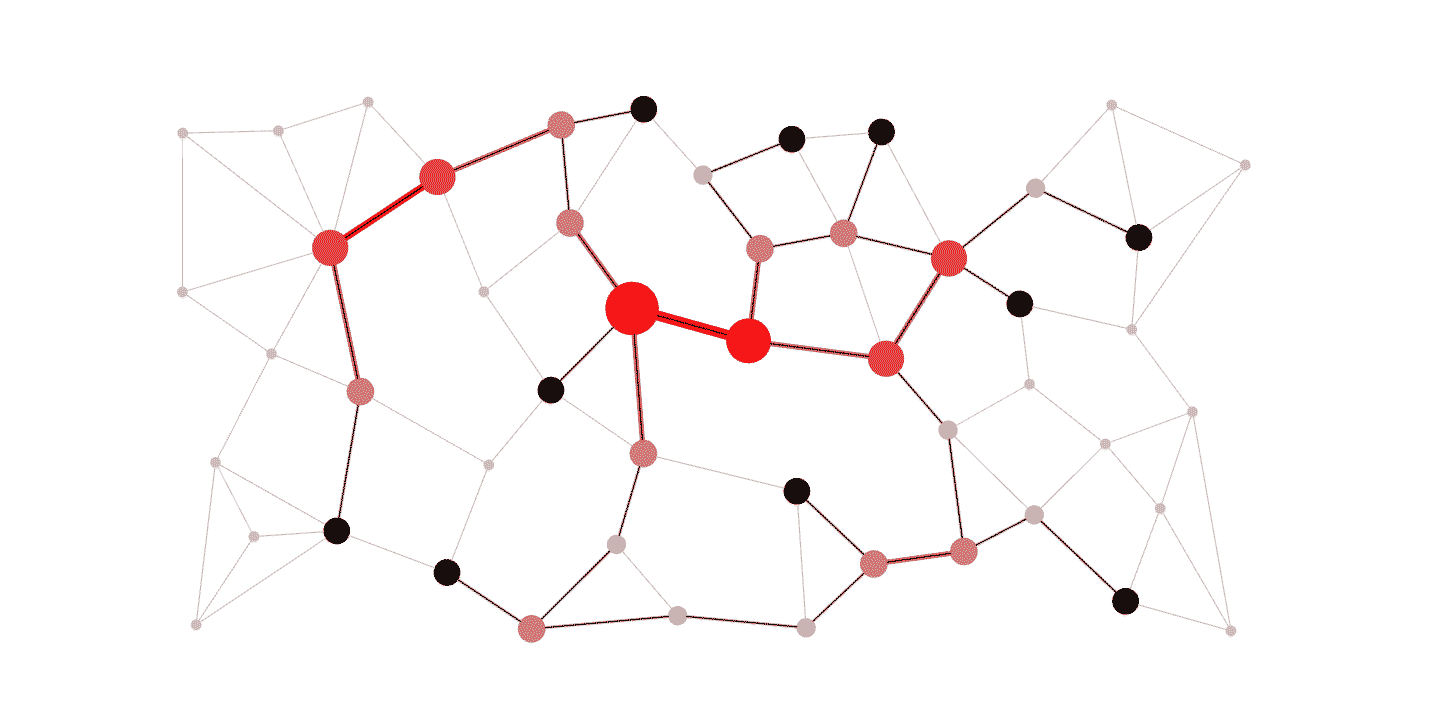 DELATOR: Money Laundering Detection via Multi-Task Learning on Large Transaction GraphsHenrique S. Assumpção , Fabrício Souza , Leandro Lacerda Campos , and 3 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) , 2022
DELATOR: Money Laundering Detection via Multi-Task Learning on Large Transaction GraphsHenrique S. Assumpção , Fabrício Souza , Leandro Lacerda Campos , and 3 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) , 2022Money laundering has become one of the most relevant criminal activities in modern societies, as it causes massive financial losses for governments, banks and other institutions. Detecting such activities is among the top priorities when it comes to financial analysis, but current approaches are often costly and labor intensive partly due to the sheer amount of data to be analyzed. Hence, there is a growing need for automatic anti-money laundering systems to assist experts. In this work, we propose DELATOR, a novel framework for detecting money laundering activities based on graph neural networks that learn from large-scale temporal graphs. DELATOR provides an effective and efficient method for learning from heavily imbalanced graph data, by adapting concepts from the GraphSMOTE framework and incorporating elements of multi-task learning to obtain rich node embeddings for node classification. DELATOR outperforms all considered baselines, including an off-the-shelf solution from Amazon AWS by 23% with respect to AUC-ROC. We also conducted real experiments that led to the discovery of 7 new suspicious cases among the 50 analyzed ones, which have been reported to the authorities.
@inproceedings{10021010, author = {Assumpção, Henrique S. and Souza, Fabrício and Campos, Leandro Lacerda and de Castro Pires, Vinícius T. and de Almeida, Paulo M. Laurentys and Murai, Fabricio}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data)}, title = {DELATOR: Money Laundering Detection via Multi-Task Learning on Large Transaction Graphs}, year = {2022}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {709-714}, doi = {10.1109/BigData55660.2022.10021010}, }
2021
-
 Predicting user emotional tone in mental disorder online communitiesBárbara Silveira , Henrique S. Silva , Fabricio Murai , and 1 more authorFuture Generation Computer Systems, 2021
Predicting user emotional tone in mental disorder online communitiesBárbara Silveira , Henrique S. Silva , Fabricio Murai , and 1 more authorFuture Generation Computer Systems, 2021In recent years, Online Social Networks have become an important medium for people who suffer from mental disorders to share moments of hardship, and receive emotional and informational support. In this work, we analyze how discussions in Reddit communities related to mental disorders can help improve the health conditions of their users. Using the emotional tone of users’ writing as a proxy for emotional state, we uncover relationships between user interactions and state changes. First, we observe that authors of negative posts often write rosier comments after engaging in discussions, indicating that users’ emotional state can improve due to social support. Second, we build models based on SOTA text embedding techniques and RNNs to predict shifts in emotional tone. This differs from most of related work, which focuses primarily on detecting mental disorders from user activity. We demonstrate the feasibility of accurately predicting the users’ reactions to the interactions experienced in these platforms, and present some examples which illustrate that the models are correctly capturing the effects of comments on the author’s emotional tone. Our models hold promising implications for interventions to provide support for people struggling with mental illnesses.
@article{SILVEIRA2021641, title = {Predicting user emotional tone in mental disorder online communities}, journal = {Future Generation Computer Systems}, volume = {125}, pages = {641-651}, year = {2021}, issn = {0167-739X}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.07.014}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167739X21002764}, author = {Silveira, Bárbara and Silva, Henrique S. and Murai, Fabricio and {da Silva}, Ana Paula C.}, keywords = {Emotional tone, Sentiment analysis, Mental health disorders, Reddit, Online communities, Emotional tone prediction}, }